Telitacicept Improves Clinical Response but Increases Infection Risk in Active SLE: NEJM
- byDoctor News Daily Team
- 28 October, 2025
- 0 Comments
- 0 Mins
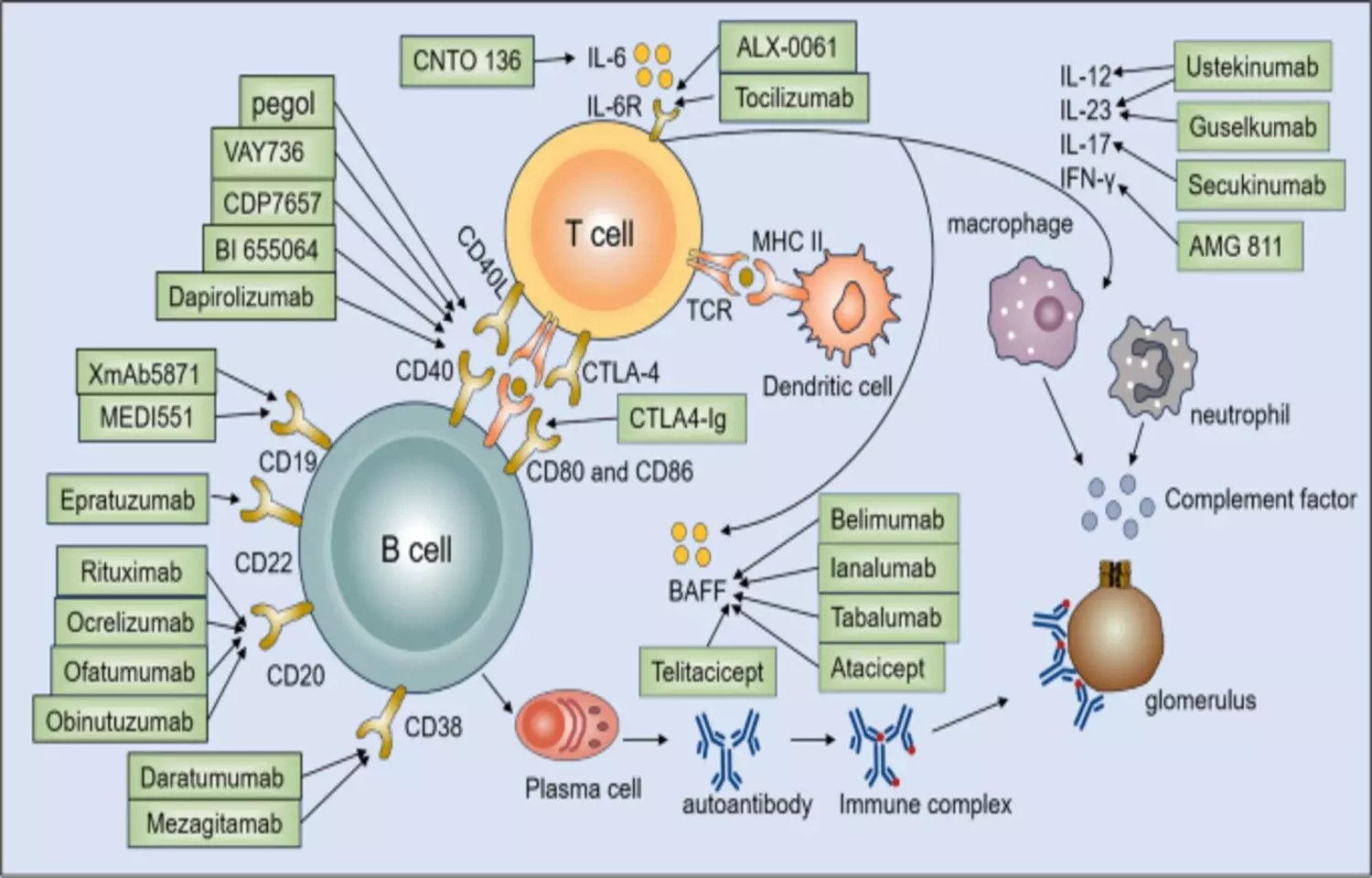
In a 52-week trial of patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) receiving standard background therapy, telitacicept produced a higher clinical response rate compared with placebo. The study, published in theNew England Journal of Medicine, evaluated the efficacy and safety of telitacicept, a dual B-cell activating factor (BAFF) and APRIL inhibitor. Patients treated with telitacicept achieved significantly greater improvements in disease activity scores, reflecting better control of lupus manifestations such as rash, arthritis, and serologic activity. However, the treatment was also linked to increased rates of upper respiratory infections, decreased immunoglobulin levels, and injection-site reactions, underscoring the need for careful monitoring. The trial demonstrated that telitacicept’s mechanism—targeting both BAFF and APRIL pathways—effectively suppresses B-cell overactivation, a key driver of autoimmunity in SLE. Compared with placebo, participants receiving telitacicept showed more frequent achievement of composite clinical response endpoints, including SRI-4 and BICLA measures. Despite the therapeutic benefit, safety data revealed that reductions in immunoglobulin concentrations could predispose some patients to infections, primarily mild to moderate in severity. Injection-site reactions were also noted but were generally self-limiting. The overall risk-benefit profile favored telitacicept, particularly for patients with persistent disease activity despite conventional treatment. In conclusion, the findings suggest that telitacicept offers a promising new approach for improving disease control in patients with active SLE, though its use requires vigilance for infection risk and immune suppression. By targeting key B-cell survival factors, telitacicept represents a significant advancement in biologic therapy for lupus. The authors emphasize the importance of individualized dosing, infection surveillance, and long-term follow-up to optimize outcomes. As further studies expand on durability and safety, telitacicept may play a pivotal role in modern lupus management. Keywords:systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE, telitacicept, BAFF, APRIL, B-cell therapy, infection risk, immunoglobulin, New England Journal of Medicine, clinical trial
Disclaimer: This website is designed for healthcare professionals and serves solely for informational purposes.
The content provided should not be interpreted as medical advice, diagnosis, treatment recommendations, prescriptions, or endorsements of specific medical practices. It is not a replacement for professional medical consultation or the expertise of a licensed healthcare provider.
Given the ever-evolving nature of medical science, we strive to keep our information accurate and up to date. However, we do not guarantee the completeness or accuracy of the content.
If you come across any inconsistencies, please reach out to us at
admin@doctornewsdaily.com.
We do not support or endorse medical opinions, treatments, or recommendations that contradict the advice of qualified healthcare professionals.
By using this website, you agree to our
Terms of Use,
Privacy Policy, and
Advertisement Policy.
For further details, please review our
Full Disclaimer.
Recent News
PG AYUSH: DME Gujarat notifies schedule for Round...
- 28 October, 2025
Delhi Doctor accused under PCPNDT Act gets court r...
- 28 October, 2025
TCT 2025: ShortCUT Trial Compares Cutting Balloon...
- 28 October, 2025
Eli Lilly Omvoh secures USFDA approval as single-i...
- 28 October, 2025
Daily Newsletter
Get all the top stories from Blogs to keep track.


0 Comments
Post a comment
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!