Oral vs. Topical TXA: Comparable Effectiveness and Safety in treatment of Melasma
- byDoctor News Daily Team
- 13 September, 2025
- 0 Comments
- 0 Mins
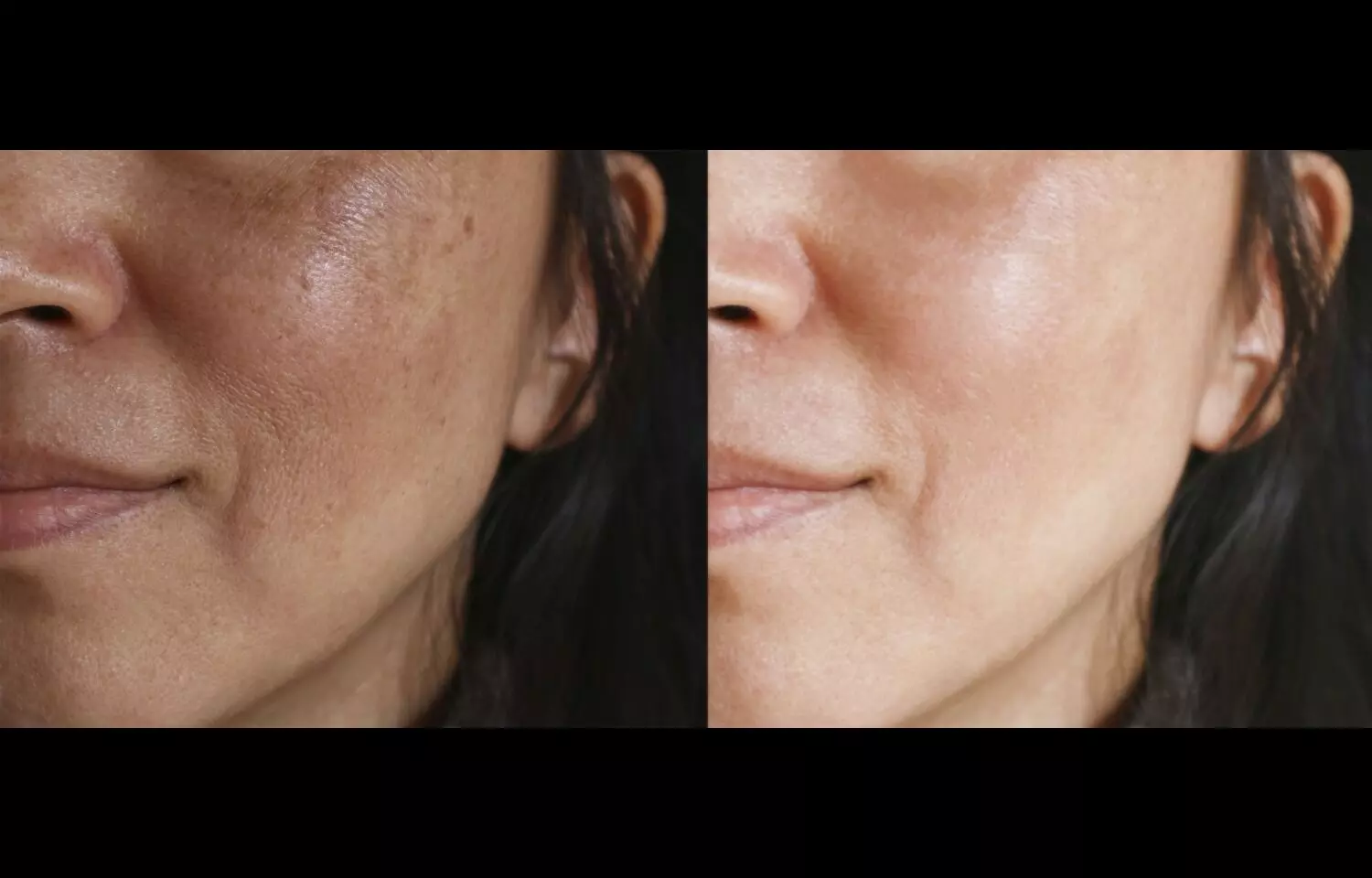
Melasma is a chronic pigmentary disorder characterized by symmetric, hyperpigmented macules and patches on sun-exposed areas, most commonly the face. It disproportionately affects women and is associated with significant psychosocial distress. Among emerging therapies, tranexamic acid (TXA), an antifibrinolytic agent with anti-melanogenic properties, has gained attention as both an oral and topical treatment option. However, comparative data on route-specific efficacy and safety have remained limited. A recent prospective study compared the effectiveness and safety profiles of oral and topical TXA in patients with moderate-to-severe melasma. Participants were randomly assigned to receive either oral TXA tablets or topical TXA formulations over a defined treatment period. Clinical improvement was evaluated using the Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI), standardized digital imaging, and patient-reported outcomes. Safety was assessed through monitoring of adverse events and laboratory parameters. Results demonstrated that both oral and topical TXA significantly reduced MASI scores from baseline, with improvements visible within the first 8 weeks and sustained throughout the study duration. Patient satisfaction scores were similarly high in both groups, indicating clinically meaningful benefit regardless of administration route. Importantly, the incidence of adverse effects was low across both arms. Mild gastrointestinal discomfort was occasionally reported in the oral TXA group, while transient local irritation was observed in the topical TXA group. No serious adverse events or thromboembolic complications were reported, reinforcing the safety profile of both approaches. The findings suggest that oral and topical TXA offer comparable efficacy in melasma treatment, with similarly favorable safety outcomes. This provides clinicians with flexibility in tailoring treatment to patient preference, tolerability, and convenience. For patients reluctant to take systemic therapy, topical TXA represents a viable alternative, while oral TXA may be preferable for those seeking systemic benefits or with extensive involvement. Overall, this study supports the role of TXA as a versatile therapeutic agent in melasma management. Long-term studies with larger cohorts are warranted to confirm durability of response and further evaluate relapse rates post-treatment.
Disclaimer: This website is designed for healthcare professionals and serves solely for informational purposes.
The content provided should not be interpreted as medical advice, diagnosis, treatment recommendations, prescriptions, or endorsements of specific medical practices. It is not a replacement for professional medical consultation or the expertise of a licensed healthcare provider.
Given the ever-evolving nature of medical science, we strive to keep our information accurate and up to date. However, we do not guarantee the completeness or accuracy of the content.
If you come across any inconsistencies, please reach out to us at
admin@doctornewsdaily.com.
We do not support or endorse medical opinions, treatments, or recommendations that contradict the advice of qualified healthcare professionals.
By using this website, you agree to our
Terms of Use,
Privacy Policy, and
Advertisement Policy.
For further details, please review our
Full Disclaimer.
Recent News
Gum disease could silently cause serious brain dam...
- 03 November, 2025
Can Early-Day Fasting Significantly Boost Metaboli...
- 03 November, 2025
Delhi HC bars doctor from running medical centre d...
- 03 November, 2025
Daily Newsletter
Get all the top stories from Blogs to keep track.


0 Comments
Post a comment
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!