Early Feeding Strategies Crucial for Preventing Early Childhood Caries, reveals research
- byDoctor News Daily Team
- 03 November, 2025
- 0 Comments
- 0 Mins
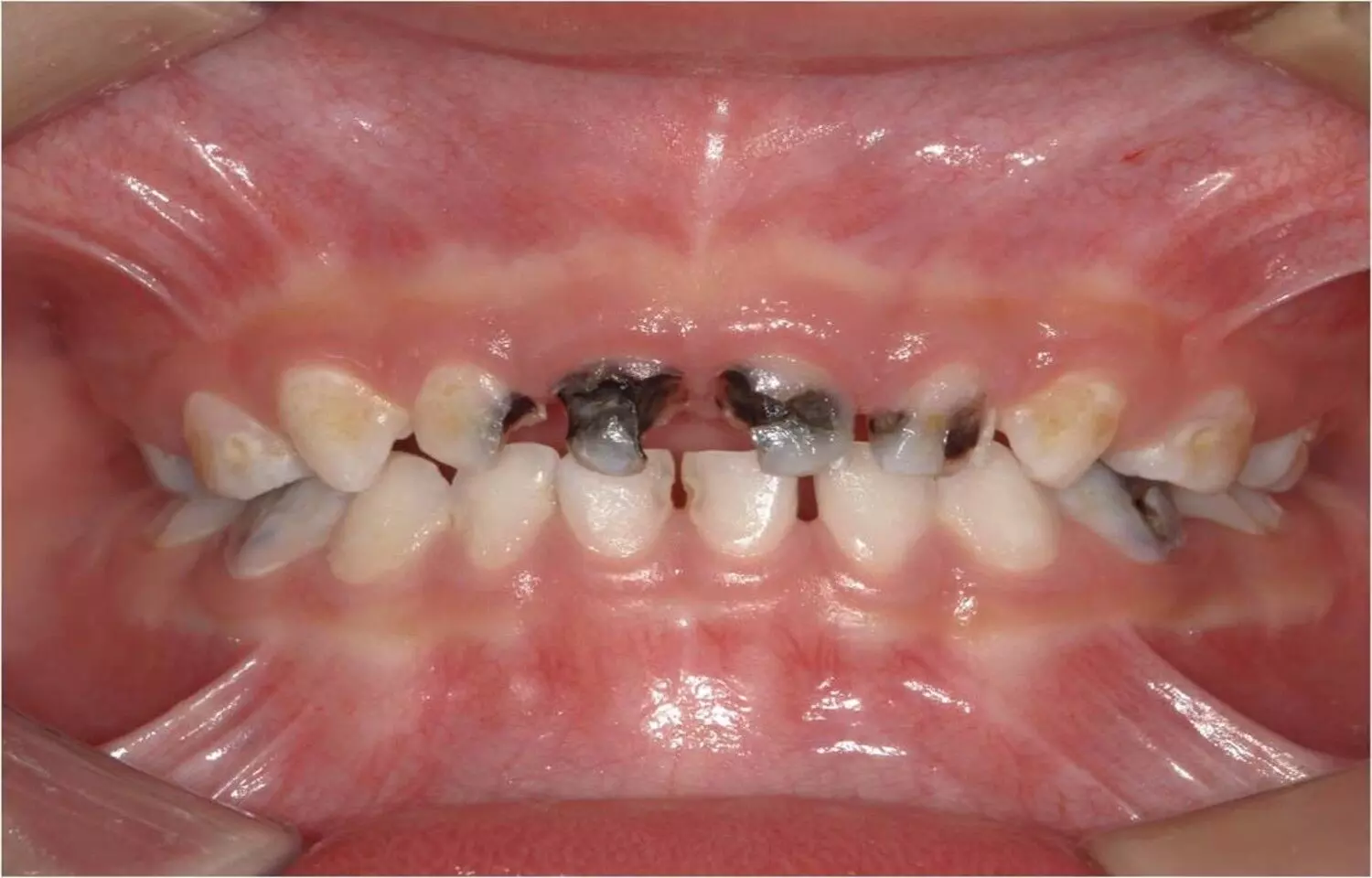
A new study published in BDJ Open has found that adopting evidence-based early feeding practices—such as reducing sugar exposure, ensuring timely introduction of complementary foods, maintaining consistent vitamin D supplementation, and promoting dietary diversity—plays a critical role in preventing early childhood caries (ECC). The findings reinforce the strong link between nutrition during infancy and long-term oral health outcomes. Researchers analyzed feeding behaviors, dietary patterns, and oral hygiene practices in young children to understand how early-life nutrition influences caries development. The study found that frequent sugar consumption, including hidden sugars in processed foods and sweetened milk formulas, significantly increases caries risk—even before teeth fully erupt. In contrast, infants who received breast milk or unsweetened formulas, along with balanced complementary foods, showed better oral health outcomes and fewer lesions.The timing of introducing solid foods also emerged as a key factor. Children who transitioned to complementary feeding at the recommended age (around six months) demonstrated healthier dental development and improved chewing habits, which aid in saliva production—a natural protective factor against caries. Vitamin D supplementation was another protective element, supporting enamel mineralization and resistance to decay.Researchers emphasized that early oral health education should be integrated into pediatric care and parental counseling. Teaching caregivers about sugar-free feeding options, proper bottle use, and early toothbrushing habits could dramatically lower ECC rates. Moreover, community-level nutrition programs and healthcare provider training can help address persistent misconceptions—such as the idea that baby teeth are “temporary” and don’t require care.
Disclaimer: This website is designed for healthcare professionals and serves solely for informational purposes.
The content provided should not be interpreted as medical advice, diagnosis, treatment recommendations, prescriptions, or endorsements of specific medical practices. It is not a replacement for professional medical consultation or the expertise of a licensed healthcare provider.
Given the ever-evolving nature of medical science, we strive to keep our information accurate and up to date. However, we do not guarantee the completeness or accuracy of the content.
If you come across any inconsistencies, please reach out to us at
admin@doctornewsdaily.com.
We do not support or endorse medical opinions, treatments, or recommendations that contradict the advice of qualified healthcare professionals.
By using this website, you agree to our
Terms of Use,
Privacy Policy, and
Advertisement Policy.
For further details, please review our
Full Disclaimer.
Recent News
Gum disease could silently cause serious brain dam...
- 03 November, 2025
Can Early-Day Fasting Significantly Boost Metaboli...
- 03 November, 2025
Delhi HC bars doctor from running medical centre d...
- 03 November, 2025
Phase III data for Gazyva/Gazyvaro show significan...
- 03 November, 2025
Daily Newsletter
Get all the top stories from Blogs to keep track.


0 Comments
Post a comment
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!